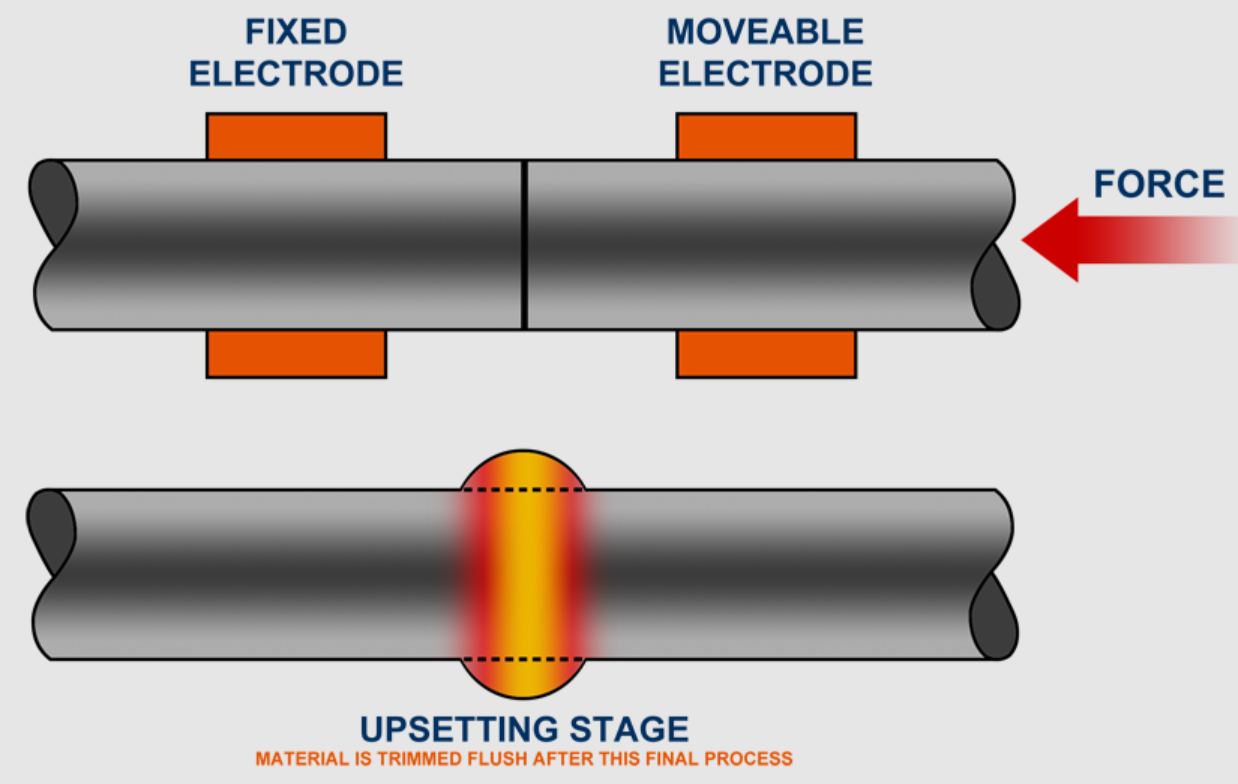
Flash butt welding is a welding technique where two pieces of metal are heated to a molten state and then pressed together. When they cool down, they fuse together and create a strong bond. In this welding technique, current pulses are created while the wheel moves along the work piece. Flash butt welding uses resistive heat created by the metal pieces themselves to connect components. The separated metal parts are then subjected to an electrical current in order to be welded. Due to resistance and an alleged arc between two work pieces, the metal subsequently begins to melt.
How Does It Work?
The clamping mechanism used by flash butt welding equipment consists of two horizontally positioned cylinders that tightly hold the rails during welding to avoid slipping and upsetting. The drawing force of the welding head is at least 100 tons. It automates the entire welding process, including flash removal and alignment. Modern welding equipment can be used on or off track to join rails with cross sections as much as 15,000 mm2.
This flashing gradually warms up and creates a softened zone at the ends of the component, clearing the contact of oxides and contaminants. After a predetermined length of parent material has been “burned off,” a forging force is applied to the parts to solidify the connection. As a result, there is no molten metal in the connection after the forge butt weld.
‘Flash time’ is the time when the arc is present. The ends of the molten metal components, that are supposed to be fused, are compelled to unite as a result of intense pressure being applied to them. The use of filler metals is not required. Based on pre-programmed parameters, an electronic control system is designed to provide a reliable welding process.
How is Flash Butt Welding Used?
 Flash butt welding techniques are most commonly used in the railroad manufacturing industry. During the following upset stroke, the rails are pushed together under intense pressure, making the ends coalesce. After the upset stroke, the upset metal is taken out. Even without the use of filler metal, this type of welding technique is incredibly precise.
Flash butt welding techniques are most commonly used in the railroad manufacturing industry. During the following upset stroke, the rails are pushed together under intense pressure, making the ends coalesce. After the upset stroke, the upset metal is taken out. Even without the use of filler metal, this type of welding technique is incredibly precise.
Due to the very narrow region of application of the heat, it is possible to achieve a uniform hardness and, as a result – a very smooth metallic structure.
What are the Benefits of the Flash Butt Welding Process?
The rail that is created is notably smoother as compared to mechanically linked rail, since there are no gaps between the sections. The flash butt welding method includes several steps, including:
- Pre-flash
- Steady flash
- Boost
- Upset
- Forging, and
- Flash material removal.
Due to the absence of joints, the welded segment has the same properties as the rest of the rail. This reduces uneven wear and strain on the rail as well as the expense and time associated with inspection and maintenance.
Constant welding process and high-quality welding connections are the result of the use of the computerized control system. The welding head is designed to provide the best quality and tolerances for stationary and in-track rail welding. Long welded rails, short welded rails and continuously welded rails – all are possible with the help of the Flash butt welding process. As a result, it is a very flexible approach.